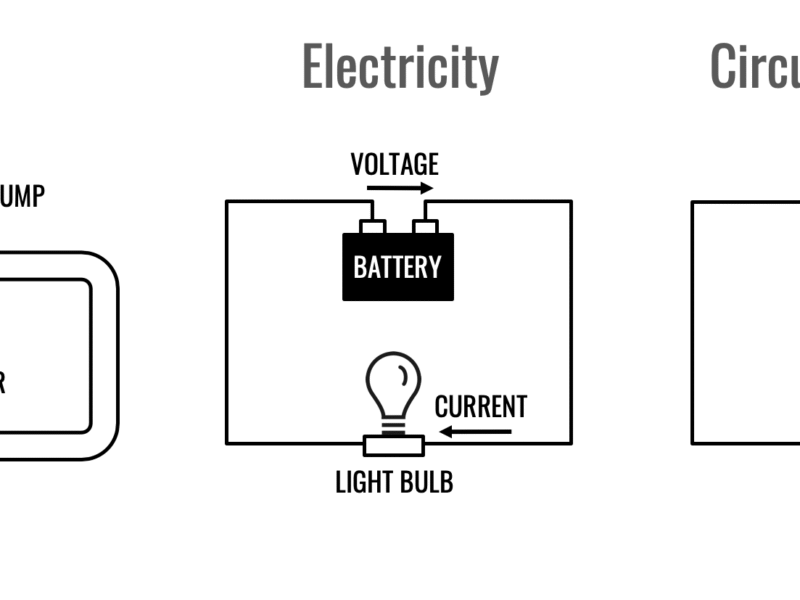
Electricity is primarily produced through the conversion of other forms of energy. The main methods include harnessing kinetic energy from moving water or wind, utilizing heat from various sources like burning fossil fuels or nuclear reactions, converting light energy directly into electricity via solar panels, and employing chemical reactions in batteries.
1. Mechanical to Electrical Conversion:
- Hydropower:Falling or flowing water spins turbines connected to generators, producing electricity.
- Wind Power:Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of wind and convert it into electricity via rotating blades connected to generators.
- Fossil Fuel Power Plants:Burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas) heats water, creating steam that spins turbines connected to generators.
- Nuclear Power Plants:Nuclear fission releases heat, which is used to produce steam that turns turbines.
- Geothermal Power Plants:Heat from the Earth’s interior is used to generate steam that powers turbines.
- Combined Cycle Plants:These plants combine gas turbines and steam turbines for increased efficiency.
2. Direct Conversion:
- Solar Power (Photovoltaics): Sunlight is converted directly into electricity using photovoltaic cells (solar panels).
3. Chemical to Electrical:
- Batteries: Chemical reactions within batteries produce electrical energy.
4. Other Methods:
- Biomass Power Plants: Burning organic matter (biomass) to produce heat and electricity.
- Wave and Tidal Power: Harnessing the energy of waves and tides to drive turbines.
- Fuel Cells: Electrochemical devices that convert chemical energy into electricity (e.g., hydrogen fuel cells).